
How Does GDPR Impact the Marketing Industry?
GDPR Implications for Marketing
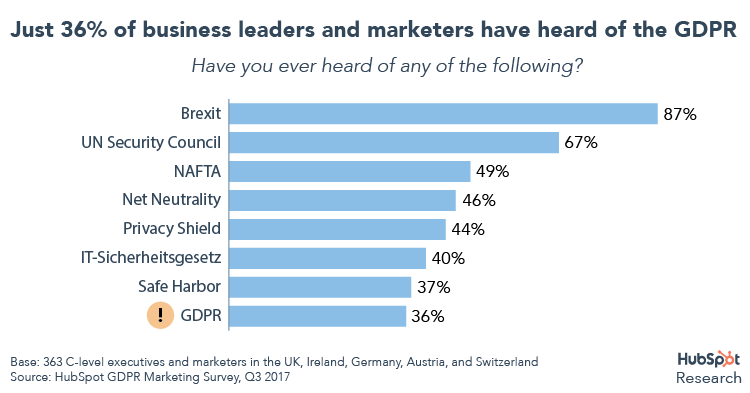
What does GDPR mean for marketing? We’re worried that not enough business leaders and marketers have heard of GDPR or have prepared for this radical privacy law because of a common misconception that GDPR is for lawyers and information security teams. But GPDR is more than a data privacy law: GDPR is a mandate that affects how organizations market, collect, use, and store consumers’ personal data, so GDPR compliance and awareness are just as important for the marketing departments as they are for IT departments. Has your business considered the GDPR implications for marketing?
What Does GDPR Mean for Marketing?
How do you know if GDPR applies to your marketing activities? Do you market or sell your products or services to EU data subjects? Even if you are based outside of the EU, GDPR applies wherever organizations process personal data of EU data subjects when providing goods or services to those data subjects or monitoring the behavior of those data subjects. There is immediate tension between GDPR requirements and marketing principles. A marketer’s goal is to gain identification information (name, email, birthday, phone number, etc.) for the purposes of promoting a good or service, but GDPR’s goal is to protect that identification information by giving data subjects control over their personal data. This tension is why there is such a need to focus on GDPR implications for marketing. What have we seen from marketers so far?
- Education: It’s hard to not see GDPR topics throughout webinars, blogs, infographics, white papers, videos, and social media. The experts are providing educational content to marketers. There’s no excuse not to learn and prepare for GDPR compliance.
- Data Mapping: Data mapping is a critical area of data privacy. It’s not practically possible to determine whether an organization is a data controller or data processor without a full knowledge of the personal data it holds, where the personal data comes from, who the personal data is shared with, and how the organization processes that personal data. Data mapping also gives you the opportunity to ensure your vendors, like email services, are also GDPR compliant. For example, take a look at Pardot’s GDPR guidance.
- Consent: When it comes to GDPR and marketing consent, a consumer must actively and freely confirm their consent. Article 7 describes consent requirements in detail, requiring organizations to demonstrate that anyone who shared personal data gave consent to use that data for activities like marketing. We’ve seen organizations revising contact forms on their webpages to include consent and sending their consumers opt-in emails to ensure they obtain consent.
- Objections to Direct Marketing: GDPR gives data subjects multiple rights over their personal data (access, erasure, and restriction – just to name a few), but the most absolute right is the right to object to direct marketing. Unlike other rights in GDPR, there are no exceptions to the requirement to cease direct marketing upon the request of a data subject. When a data subject objects to direct marketing, organizations must grant that request.
- Update Privacy and Notices: Have you received a flood of updated privacy policies from brands you are subscribed to? This is one way that many organizations are addressing GDPR’s requirement to ensure transparency about their data uses so that data subject’s can make an informed decision about whether or not to share their personal data. Check out Twitter’s FAQ for its approach to GDPR.
Benefits of GDPR for Marketers
Although GDPR presents challenges for marketers and many are intimidated by the GDPR implications for marketing, compliance also brings many benefits.
- Building customer trust is a difficult task in this day and age; digital consumers are fearful of unwanted follow-up, sales pitches, cold calls, and spam. GDPR compliance is an opportunity to present your organization as a secure and trustworthy service or source, and even has the potential to rebuild the trust that many digital consumers have lost. This trust may actually result in greater sharing of personal data.
- Complying with GDPR pushes marketers to put the user experience first and demonstrate that you respect user preferences. With GDPR enforcement on the rise and its data privacy controversies, Facebook, Uber, and Wells Fargo have all begun advertising campaigns that attempt to demonstrate their dedication to putting the user experience first.
- GDPR compliance gives marketers the opportunity to improve their data security as they engage with prospects and consumers.
- Because email marketing strategies may need to be shifted for GDPR compliance, this gives marketers an opportunity to focus on areas that may not be so heavily impacted by GDPR, like social media, SEO strategies, and content creation.
- GDPR compliance may bring a competitive advantage for two reasons. First, meeting GDPR compliance demonstrates to prospects and consumers that your organization prioritizes data security and user privacy. Second, once you’ve taken steps towards GDPR compliance, you can reduce the likelihood that your organization or your clients will face regulatory investigations and fines.
GDPR has a worldwide impact that will change the way organizations collect, use, store, and secure personal data. Want to learn more about GDPR implications for marketing? Contact us today to speak with a privacy expert.
More GDPR Resources
The rules around business to business marketing, the GDPR and PECR
Auditor Insights: Are you a Data Controller or a Data Processor?