According to the Department of Health and Human Services Office for Civil Rights’ “wall of shame,” data breaches and security incidents have impacted more than 450,000 individuals so far this year. With no solution or end to the pervasive threat landscape in sight, this begs the question: what more could the healthcare industry do to protect their patients’ PHI, provide quality healthcare services, and ensure that their security posture remains strong against the threats of hackers and human error? We believe that investing in penetration testing will support healthcare entities, both covered entities and business associates alike, to ensure HIPAA compliance.
What is Penetration Testing?
With an increasing number of data breaches and security incidents being reported to the OCR, the healthcare industry has a responsibility, now more than ever, to protect their sensitive assets. PHI, security systems, expensive research and prototypes, drugs, scheduling information, and operations of facilities – they’re all vulnerable to malicious hackers. By undergoing penetration testing, organizations will be able to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities that could result in access to ePHI. What exactly is penetration testing?
Penetration testing is a critical line of defense when protecting your organization’s sensitive assets from malicious outsiders. It is the process of performing authorized security testing, or ethical hacking, of an environment to identify and exploit weaknesses associated with the targeted systems, networks, and applications before those weaknesses can be exploited by a real attacker. Ultimately, penetration testing is a proactive step covered entities and business associates can take in support of their HIPAA compliance efforts.
Penetration Testing and HIPAA Compliance: Is it Required?
Although penetration testing is not explicitly required in order for covered entities and business associates to maintain HIPAA compliance, according to 45 CFR 164.308(a)(8), covered entities and business associates should “perform a periodic technical and nontechnical evaluation, based initially upon the standards implemented under this rule and subsequently, in response to environmental or operational changes affecting the security of electronic protected health information, that establishes the extent to which an entity’s security policies and procedures meet the requirements of this subpart.” Here, the technical evaluation is often interpreted as security testing like vulnerability assessments and penetration testing.
Case Studies: Penetration Testing for HIPAA Compliance
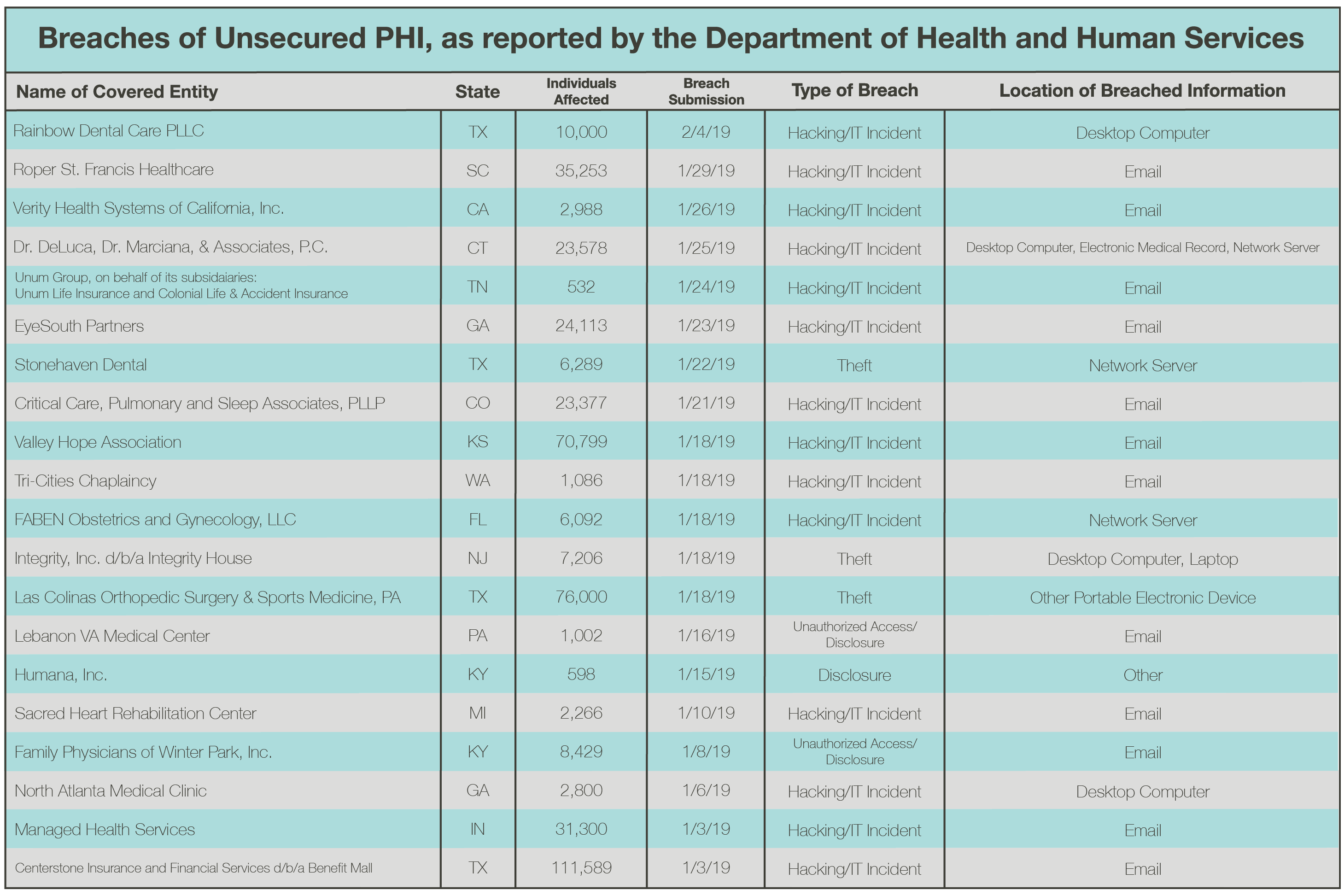
Not convinced that your healthcare entity needs to undergo penetration testing? Take a look at these recent breaches and how the organizations could have benefited from some form of penetration testing.
- BenefitMall, a business associate, fell victim to a phishing attack that left 111,600 individuals at risk. Undergoing social engineering would have been a proactive way this organization could’ve prevented this from happening. Do your employees know how to identify and withstand a phishing attempt?
- Valley Hope Association, a healthcare provider, experienced a breach where malicious outsiders gained unauthorized access to email messages and file attachments stored in an employee’s email account, impacting almost 71,000 individuals. What network protections do you have in place to protect hackers from getting in?
- DeLuca, Dr. Marciano & Associates, P.C., a healthcare provider, experienced a ransomware attack that infected two servers containing PHI and impacted nearly 24,000 customers. Ransomware is a major threat to the healthcare industries. What devices, systems, and networks could ransomware enter at your organization?
- All-Star Orthopaedics, a Texas-based Las Colinas Orthopedic Surgery and Sports Medicine center, notified the OCR that an unencrypted hard drive containing the PHI, such as X-rays, names, and dates of birth, of 76,000 patients was stolen. Are your hard drives encrypted? What security measures do you have in place to ensure they’re secure?
Need further proof that security testing is vital to healthcare organizations? The number of breaches reported to the OCR just keeps growing. Penetration testing may have changed the outcome of the following breaches.
If you’re a covered entity or business associate committed to HIPAA compliance, we’re here to help! Contact us today to learn how our penetration testing can take your security to the next level and keep your name out of the headlines.
More Penetration Testing and HIPAA Resources
7 Reasons Why You Need a Manual Penetration Test
Not All Pen Tests Are Created Equal
How Can Penetration Testing Protect Your Assets?
HIPAA Compliance Checklist: Security, Privacy, and Breach Notification Rules



